The return on investment (ROI) with lean manufacturing can be significant, although the specific amount will vary depending on the company, industry, and implementation approach. By reducing waste, improving efficiency, and increasing productivity, lean manufacturing can result in a variety of cost savings and revenue generation opportunities.
- Reduced costs: By eliminating waste and improving efficiency, lean manufacturing can reduce costs associated with excess inventory, overproduction, waiting times, and defects. This can result in significant savings on materials, labor, and other resources.
- Improved quality: Lean manufacturing focuses on producing high-quality products with minimal defects. This can lead to reduced costs associated with rework, warranty claims, and customer returns, as well as improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased productivity: Lean manufacturing can help streamline production processes, reducing cycle times and increasing throughput. This can result in increased productivity and capacity, allowing companies to produce more with fewer resources.
- Improved employee engagement: Lean manufacturing involves a culture of continuous improvement and employee involvement. This can lead to improved morale, job satisfaction, and retention, as well as increased innovation and problem-solving capabilities.
Overall, the ROI associated with lean manufacturing can be substantial, with many companies reporting cost savings and revenue generation opportunities in the range of 20-50% or more. However, it is important to note that implementing lean manufacturing requires a significant upfront investment in time, resources, and training, so companies should carefully evaluate the costs and benefits before proceeding.
1Toyota Production System (TPS)
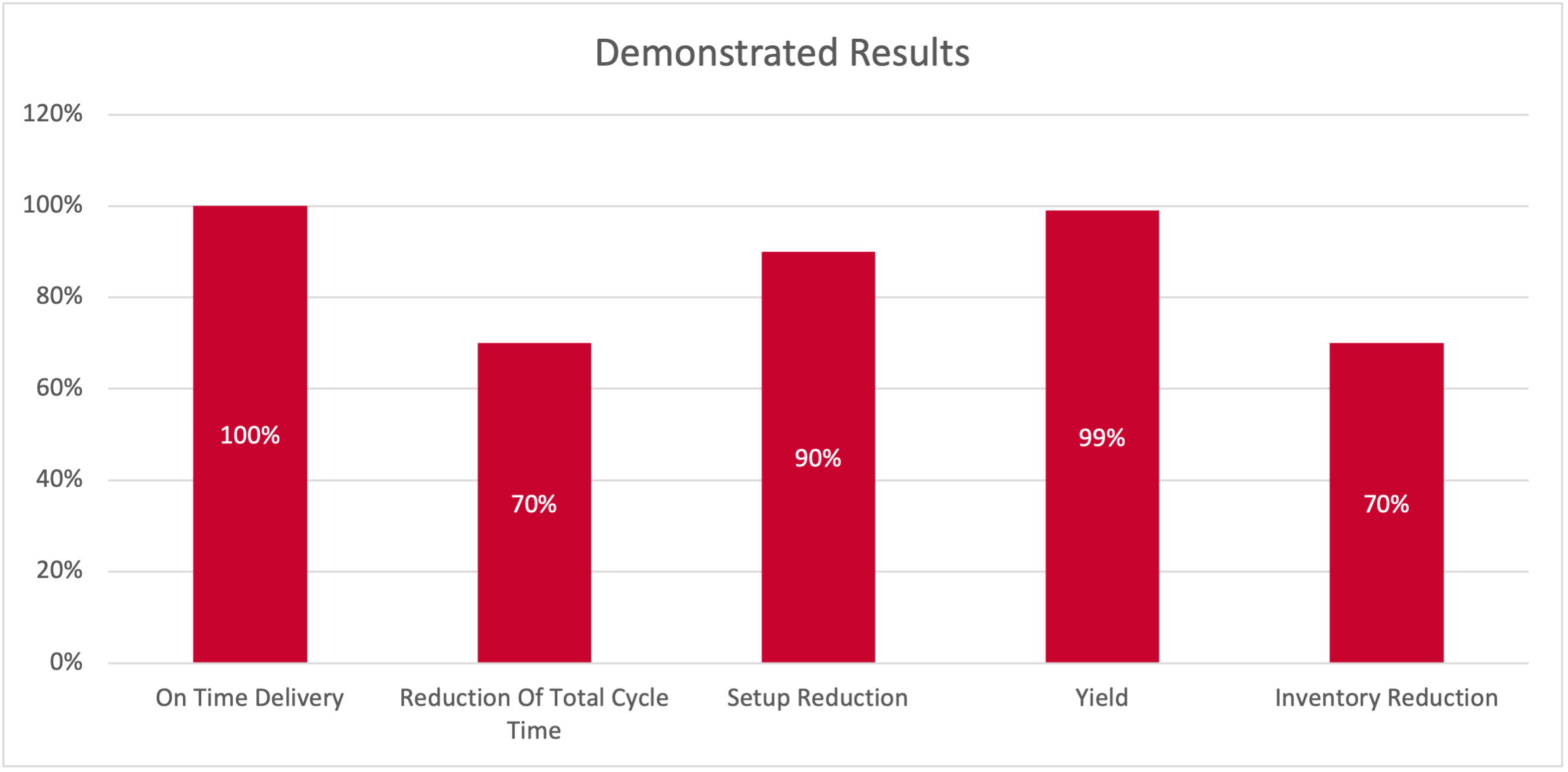
Improved liquidity and working capital
2Constraint Management - Theory of Constraints
Leadtime reduction – order to cash
35S
Eliminate waste
4Kaizen
Improve throughput
5SMED (Single Minute Exchange of Dies)
Reduce lot sizes
6One Piece Flow
Creates straight time capacity
7Problem Solving/Root Cause and Correction Action
Creates stable processes
8Kanban
Reduce inventory
Lean manufacturing is a business philosophy that focuses on maximizing value for the customer while minimizing waste. It originated in the manufacturing industry but has since been applied to a wide range of industries.
The fundamental principle of lean manufacturing is to eliminate waste from the production process. Waste, in this context, refers to any activity or resource that does not add value to the product or service being offered. Examples of waste include excess inventory, overproduction, unnecessary motion or movement, waiting times, and defects.
To implement lean manufacturing, companies typically follow a set of principles, including:
- Identify customer value: This involves understanding the needs and expectations of the customer and designing products and services that meet those needs.
- Map the value stream: This refers to analyzing the entire process of delivering a product or service, from the initial concept to the final delivery to the customer. The aim is to identify areas of waste and inefficiency.
- Create flow: Once the value stream has been mapped, the goal is to create a smooth flow of work through the process, minimizing waiting times, bottlenecks, and interruptions.
- Establish pull: This involves creating a demand-driven system in which products are produced only when they are needed, based on customer demand.
- Seek perfection: Continuous improvement is a key element of lean manufacturing. Companies should always strive to eliminate waste and improve the efficiency and quality of their processes.
Overall, the aim of lean manufacturing is to create a culture of continuous improvement and waste reduction, leading to higher quality, lower costs, and greater customer satisfaction.
Company of Professionals
Mike and Will are here to help ease your pain points. Let us know how we can help!





