Core Concept
The core concept of the Theory of Constraints is that every process has a single constraint and that total process throughput can only be improved when the constraint is improved. A very important corollary to this is that spending time optimizing non-constraints will not provide significant benefits; only improvements to the constraint will further the goal (achieving more profit).
Thus, TOC seeks to provide precise and sustained focus on improving the current constraint until it no longer limits throughput, at which point the focus moves to the next constraint. The underlying power of TOC flows from its ability to generate a tremendously strong focus towards a single goal (profit) and to removing the principal impediment (the constraint) to achieving more of that goal. In fact, Goldratt considers focus to be the essence of TOC.
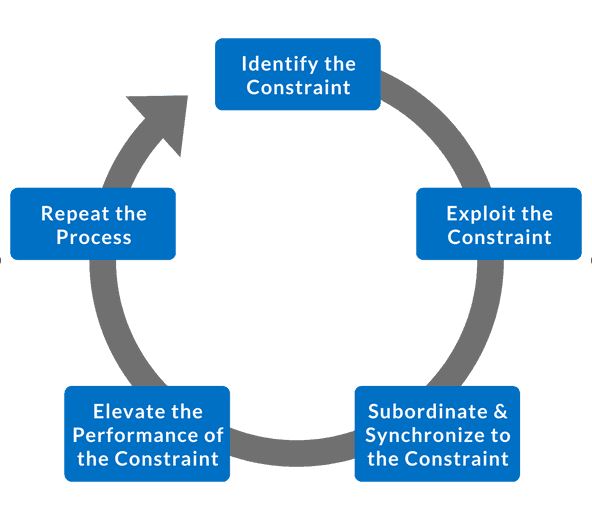
The Five Focusing Steps
The Theory of Constraints provides a specific methodology for identifying and eliminating constraints, referred to as the Five Focusing Steps. As shown in the following diagram, it is a cyclical process.